I am trying to illustrate two incidents in front of you
- A crime happened at a site. Criminal escaped but left the sign of his presence unknowingly. A single fragment of hair. Now, as a biochemist you need to analyse this tiny fragment. But it’s just a tiny fragment! The quantity is very small and so it become almost impossible to analyse this properly. What to do now?
- Suppose, you have a small fragment of DNA of an endangered plant. But for proper research or synthesis this DNA you need proper amount of the DNA. What to do now?
Here are two problems, but Do you know solution is one?
And the solution is PCR (POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION)
What is PCR?
PCR is a method used to produce more copies (millions, billions copies) of a specific DNA sample.
But we can also produce more copies of DNA by gene cloning method.
Why not Gene cloning? Why choose PCR method?
Time saving.
Yes, huge time can be consumed by using gene cloning method. That’s why for quick results PCR method considered best.
Requirements of PCR method
1) PCR machine-Thermocycler

For different stages of the PCR method (which we will know later) different temperature is need. This machine help to increase or decrease the temperature which is programmed manually.

b) Enzymes:- What enzymes actually need that already given in the name of the method. PCR- Here “P” – stands for polymerase, specifically Taq polymerase (Isolated from a thermostable bacterium called Thermus acquaticus) and the vent polymerase (From Thermococcus letoralis).
Do you know why this specific polymerase need?
Just look at the temperature graph (PCR temperature cycle) once again. High temperature (almost 95°C, 70°C) is required at this method. Taq polymerase and vent polymerase can survive at this temperature. That’s why they are called thermostable polymerase. Taq polymerase is mostly used.
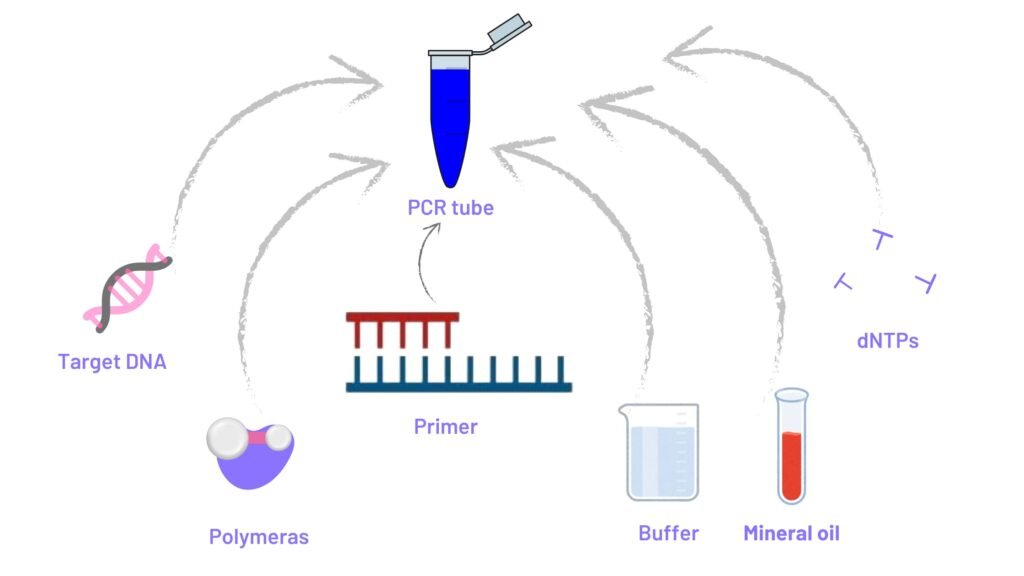
c) PCR components-reaction mix:
Target DNA:- This DNA is amplified in PCR machine,
Primers:- Primers are short nucleotide which is nearby 18-30 nucleotide long with similar G+C contents (more G+C DNA sequence means more stability). This primers bind to target strands for producing more copies. Primers should not be too long or too short
dNTPs(deoxy Nucleotide TriPhosphates):- Play role as a building block of new DNA sequesnce. There are four types of dNTPs used in the PCR; deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP), deoxyguanosine triphosphate (dGTP), deoxythymidine triphosphate (dTTP), and Deoxycytidine triphosphate (dCTP)
Reaction buffer:- This actually help to increase reaction efficiency and prevent the formation of secondary structure. Basic components of PCR buffers are Dimethyl sulfate (DMS) (CH3O)2SO2, Ammonium sulfate (NH4)2SO4, Non-ionic detergents, Polyethylene glycon (PEG), N,N,N-trimethylglycine (betaine), Magnesium chloride (MgCl2), Potassium chloride (KCl), Tetramethylammonium chloride, Tris – HCl, Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), 7-deaza-2′-deoxy-guanosine-5′-triphosphate, glycerol (C3H8O3), Formamide (CH3NO), serum albumin, etc
d) Taq polymerase and
e)Mineral oil:- To improve heat conductivity.
This all components in proper amount put in a PCR tube, which tube is placed in PCR machine for further processing.
Denaturation (Melting of target DNA):- In easy word, Denaturation means transform or modify. So, in this step of PCR of course some modification will happen, right?
Actually, the hydrogen bond of target DNA breakdown and separation happens because of high temperature (90 °C – 95 °C, for 15 second).At last of this step we found two strands which will act as a templates.
Primer Annealing:- You can also say annealing as binding. In the this step binding of a pair of oligoneucleotide primers to the DNA strands which has denatured in the first step.
These primers attach to their complementary sequence. There are two types of primers. Forward primer and Reverse primer.
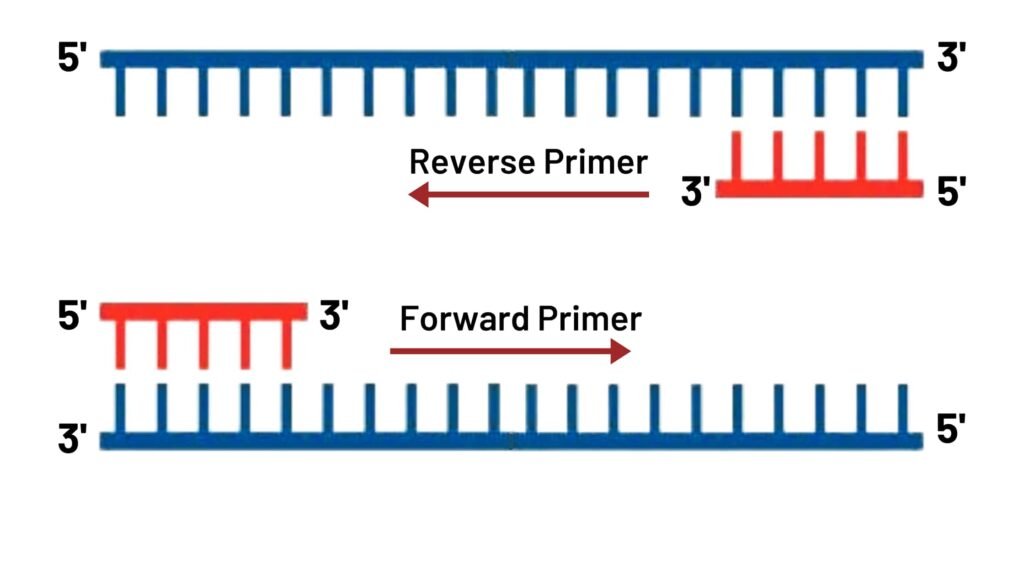
In this picture, primers attach to template DNA strands. The primer that going in forward direction is known as forward primer and other one is reverse primer. 5‘ of primer add with the 3‘ of the DNA templates.
Extension :- This step also known as Polymerization. At PCR machine, at this step, temperature rise to 72°C and this is optimum temperature for Taq polymerase. Optimum temperature means the temperature at which an enzyme works best and help to produce more products. Taq polymerase now get the chance to work best. This enzyme now find out the primers, attach to these and elongate the primer by adding DNTP’s that we have already mixed in the PCR tube. That’s how we found two new strands finally.
One cycle is done after the completion of three steps. And the three steps cycle is repeated
After first cycle 2 (21) new DNA strands is found. From this two strands, 4 (22) copies yields in the next cycle. That means every cycle generating 2n molecules of DNA (n is the number of cycle). This cycle is repeated about 50 times. About one millions copies will produce after 20 cycles and nearby one billions copies will produce after 30 cycles. Exponential growth. Within short time (in 75 minutes 105 times) huge number of DNA copies found by this method.